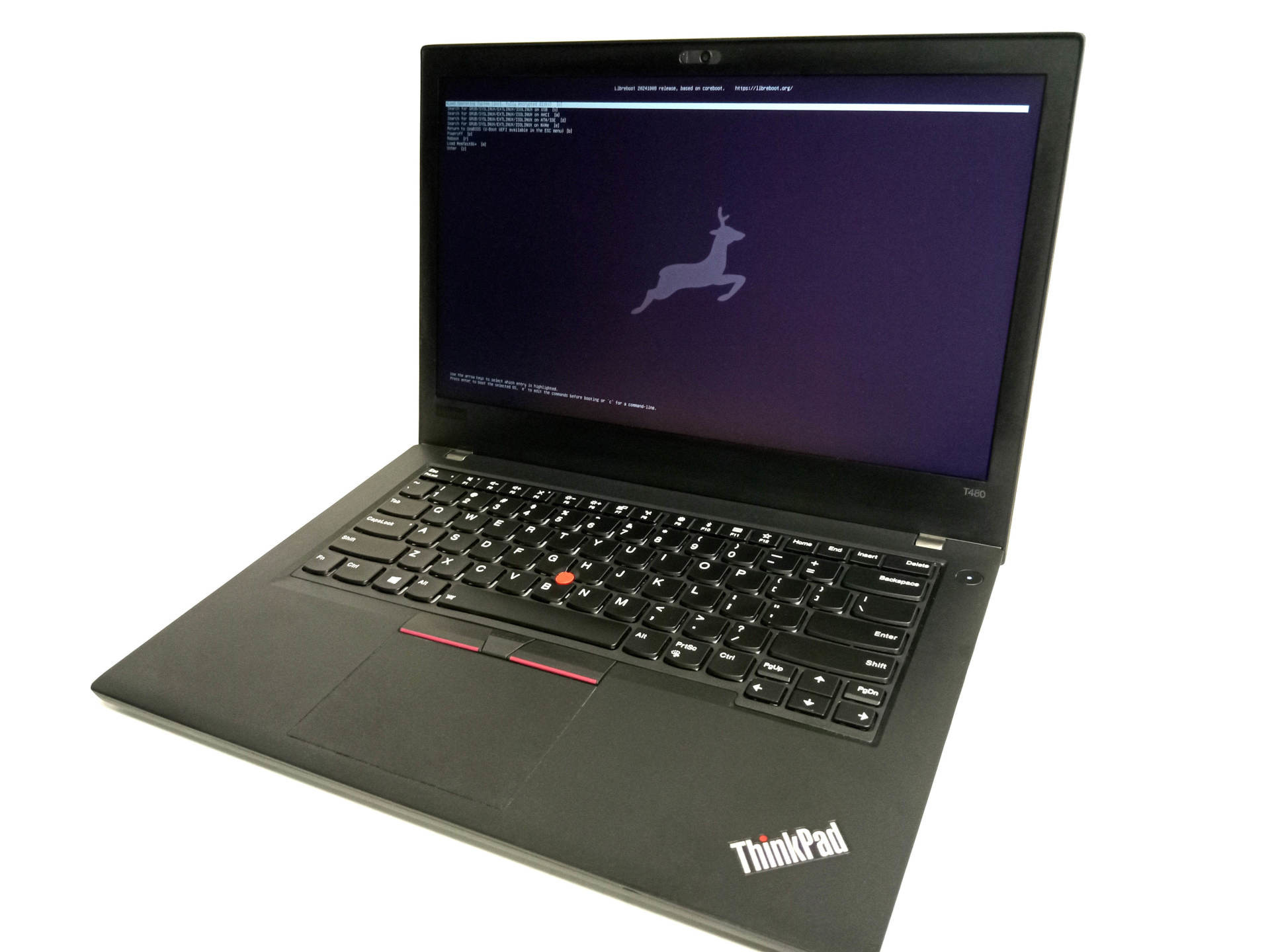
Libreboot T480 with 4-core i5-8250u, Intel UHD 630 graphics, 32GB/64GB DDR4 RAM, Intel AX210 WiFi, 1TB/2TB NVMe SSD and Debian Linux
- Main products:
- Libreboot T480
- Libreboot T580
- Libreboot 3050 Micro
- -
- Contact Minifree to place an order
| Prices | |
|---|---|
| 16GB RAM, 240GB NVMe | £498+VAT (British pounds) |
| 32GB RAM, 1TB NVMe | £758+VAT (British pounds) |
| 64GB RAM, 2TB NVMe | £998+VAT (British pounds) |
| Shipping: | International shipping available |
| 0% VAT: | 0% UK VAT for International shipping addresses |
| 20% VAT: | 20% UK VAT for British shipping addresses |
| How to purchase: | Email us for an invoice |








| Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Lenovo |
| Model | ThinkPad T480 |
| Free boot firmware | Libreboot |
| Chipset | Intel Kaby Lake Refresh |
| CPU | Intel i5-8250u |
| Graphics | Intel UHD 630 |
| Screen resolution | 1920x1080 IPS |
| Memory | DDR4 SODIMM |
| Architecture | x86_64 |
| Intel ME | Disabled with me_cleaner. |
| Flash chip | SOIC-8 16MiB (128Mbit) |
| Battery life | At least 50Wh |
| Connectors | |
|---|---|
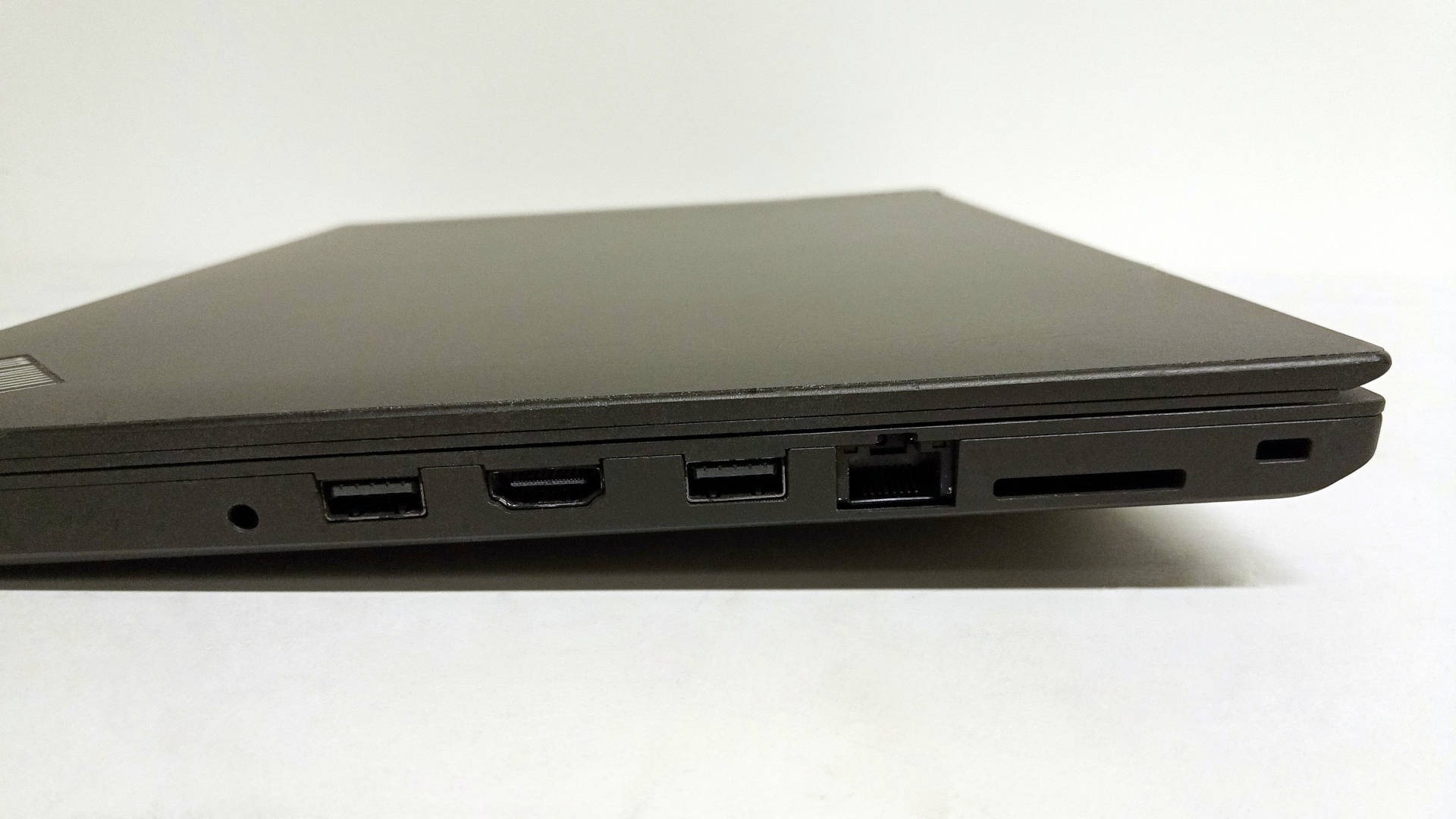
| Video | HDMI, ThunderBolt, USB-C |
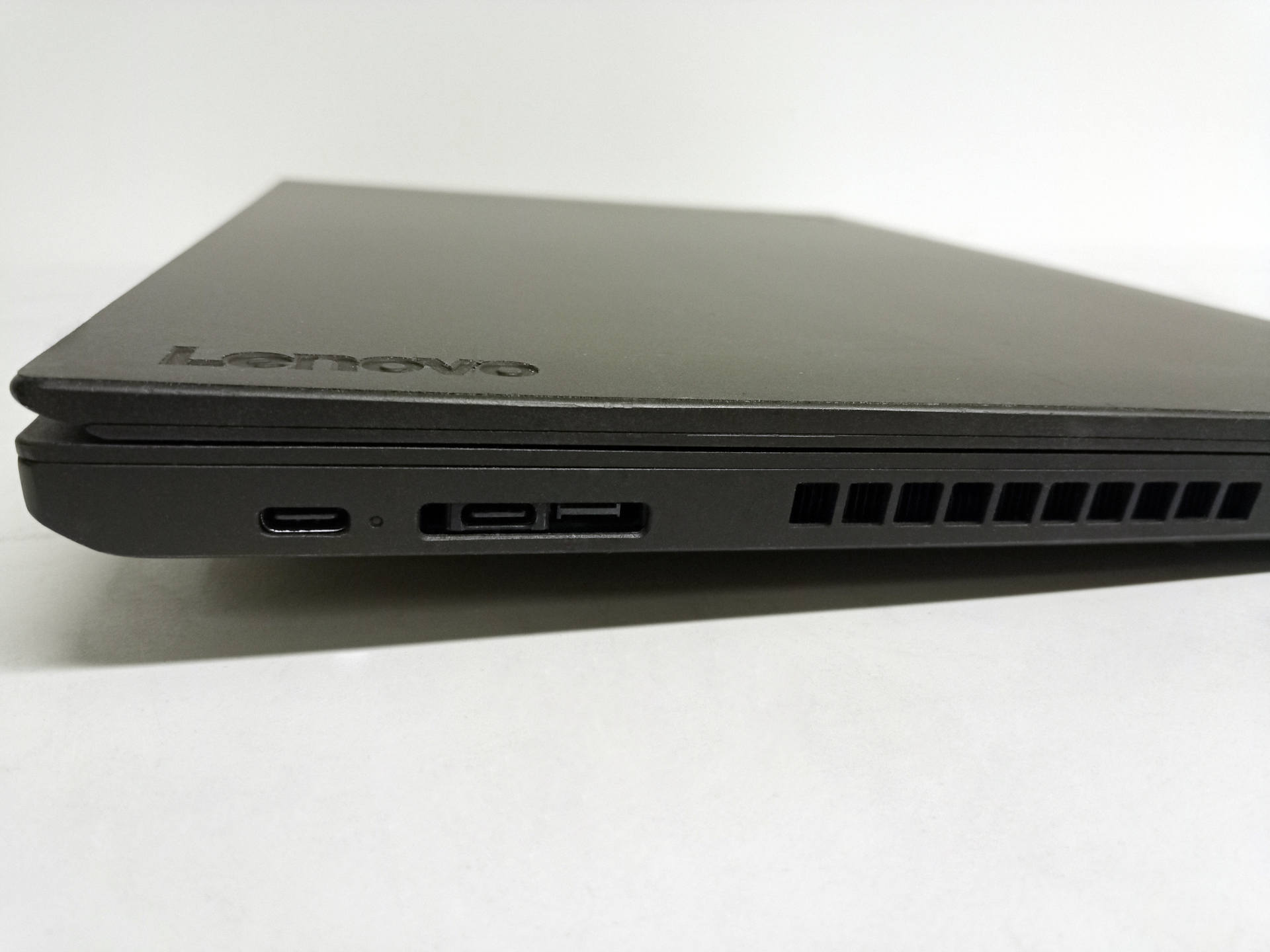
| USB | 2x USB 3.0, 1x USB-C |
| DC input | 1x USB-C, 1x ThunderBolt, 2x battery |
| WiFi | 2 internal antennae |
| Ethernet | 1x RJ-45 (Intel I219-V) |
| Audio | 2x 3.5mm (1 line-out, 1 line-in) |
| DP(USB-C)/HDMI audio | Works |
| Accessories | |
|---|---|
| Power supply | 65W DC 20V output, 120/240V AC input |
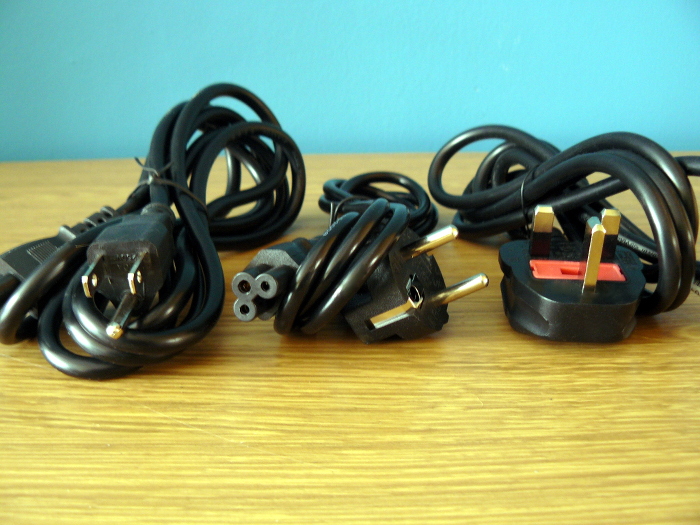
| Power cable | US, EU, UK as necessary |
Shipping worldwide! Minifree ships internationally from the UK. We ship to Europe, UK, USA, Canada, and everywhere else including Asia. We even ship to Australia!
The Libreboot T580 was recently launched, which may also interest you; bigger screen and full-sized keyboard.
Minifree Ltd (based in the United Kingdom) sells secure, high quality computer systems with Free, Libre, Open Source Software (FOSS) pre-installed. Libreboot BIOS/UEFI replacement (based on coreboot) and encrypted Debian GNU+Linux OS pre-installed (KDE Plasma desktop environment), with full driver support. These machines are intended for security-conscious people who also believe in the ideals of the free software movement, and want something easy to use. Perfect for privacy software like Tor Browser or Tails; you can also run Qubes OS on these machines. BSDs also work well.
Leah Rowe, the owner of Minifree, is also the founder of Libreboot, and lead developer; Minifree profits directly fund the Libreboot project.
This is a high-performance workstation based on heavy modification of the Lenovo ThinkPad T480. It comes with Libreboot pre-installed, which replaces proprietary BIOS/UEFI firmware, offering greater security and fast boot speeds. Debian Linux pre-installed (operating system). Available to order, shipping worldwide!
This product is intended for those security conscious people who believe in the ideology of software freedom, and want a truly privacy-respecting computer product that is easy to get started with. You control your Libreboot machine, not the other way around. It is your property. KDE Plasma desktop environment provided by default, along with common applications such as web browser, productivity suite, text editors and so on. You can easily install from tens of thousands of available software packages via your Linux distro’s package manager, if you wish, for a given computational task that you wish to perform. KDE is a well-respected and powerful desktop environment, yet easy to use even for novice computer users.
Shipping worldwide! Minifree ships to USA, Canada, South America, Europe, Australia, Asia, and everywhere else, shipping globally from Minifree’s lab in the United Kingdom. Free 5 year warranty provided on all orders. The correct power cable is provided (e.g. USA, EU, UK), for each customer; the power supply is 120-240V auto-switching, so it works in every country. A compatible 65W DC power supply will be provided.
Your freedom. Your Libreboot.

Most people use proprietary boot firmware, even if they use free operating systems. Many computers today are known to contain malware, chief among them being Intel’s Management Engine (ME). Our systems are different. Your Libreboot system will never spy on you, and it will never leak your data to anyone. Your privacy and security is critical. You are the owner of your machine. We believe free software is a fundamental right, something that everyone must have.
Your Libreboot T480 obeys you, and nobody else! It’s Libreboot inside! The Intel ME is disabled on every machine, using me_cleaner which disables the ME after BringUp – this is done for your security, and privacy. You have the freedom to tinker with every part of the machine; full source code is also available, for Libreboot and the installed Linux/BSD operating system of your choice.
Additionally: this machine makes use of the excellent deguard utility, alongside me_cleaner. Deguard disables the Intel Boot Guard, which is the reason why coreboot (and therefore Libreboot) can support this hardware!
WiFi upgrade
Intel AX210 WiFi included by default, for fast WiFi 6 performance. More information about this card is available on Intel’s website:
This card can reach 1Gbps throughput, in Minifree’s testing. It’s a really fast wireless card.
Why use these machines?
These machines are provided because we in the Free Software movement believe Free Software is a right that everyone must have; free refers to freedom. It is software for which source code is available that you can freely use, study, modify and share without restriction. These machines are intended for security-conscious people who value the ideals of the free software movement, and want something easy to use that is in the control of the user (not the vendor). Free software is a global movement that started in the 1980s with the BSD and GNU projects, but its roots go all the way back to the very early days of computing; free software is used and developed today by millions of people, and it runs some of the most critical infrastructure on the internet.
Many people nowadays use bloated, inefficient software, a description that often applies to proprietary software; Free Software isn’t beholden to corporate greed, and many of the people who work on it care passionately about writing the most well-audited, high quality code. Modern versions of Windows use gigabytes of RAM, whereas a Linux/BSD system with a lightweight (yet modern) desktop environment will use far less than that, aswell as few CPU cycles and disk I/O; in other words, Linux systems can have much lower system requirements. Minifree shares in this lightweight software design philosophy. Libreboot itself (lead by the same person who owns Minifree) is designed to be as simple as possible, in terms of project infrastructure, build system, and actual coreboot configuration, providing firmware that boots as quickly as possible, and with a simple user interface (SeaBIOS and/or GRUB payload) that most people can just use, intuitively. Libreboot heavily patches the various upstream projects used, such as coreboot and GNU GRUB, fixing various upstream issues and providing more reliable operation for the user.
Libreboot releases focus on stability, providing well-tested firmware that is rock-solid on all of the supported hardware, and with a unified user interface across (where possible) all boards. That means, if you learn to use one Libreboot system, you can most likely use another with little fuss. Libreboot does away with nasty anti-features such as UEFI SecureBoot (nasty because it makes using free operating systems harder), instead implementing its own optional security methods that are completely within the user’s control, such as GPG signature checking of your Linux kernel from GRUB, which runs directly in the flash (which you can write-protect, if you wish), or the ability to have true Full Disk Encryption, including /boot. In most setups (on x86 hardware), Libreboot directly boots GNU GRUB from the flash (with its own config file), which is configured to automatically find and boot your distro’s own GRUB, EXTLINUX or SYSLINUX configuration (and manual configuration is possible), even in cases where it resides in an EFI System Partition (ESP), or a btrfs sub volume – GRUB is extremely powerful in this setup, as a coreboot payload, more flexible than any standard BIOS- or UEFI-based setup, and it works because Linux/BSD systems are able to run directly on bare metal, without calling into BIOS/UEFI. Libreboot provides a direct video framebuffer, that any operating system can use if it supports Kernel Mode Setting (all Linux/BSD systems do nowadays). This is a much cleaner way to boot your operating system, and GRUB is highly efficient.
A coreboot payload called SeaBIOS is also provided, which you can optionally use (useful for BSD bootloaders, prior to loading the BSD kernels). SeaBIOS implements a standard x86 PC BIOS, whereas GRUB provides multiboot functionality to directly boot a Linux kernel (along with drivers for the disk, filesystem, etc – and an often overlooked but extremely powerful user shell, that behaves very similarly to a full BASH shell with many commands available – more info available in the GRUB documentation, though Minifree configures these systems to Just Work so you can simply turn them on and use them).
Libreboot even includes MemTest86+ directly in the flash! You can boot it from the GRUB or SeaBIOS payload. No more messing about with bootable USB media. It comes preinstalled! Coreboot is very different than proprietary firmware, in that you can run whatever you want. You’re not restricted to whatever the vendor gives you. You could even compile your own OS (e.g. Linux with busybox/musl) and put it in the flash, if you wanted to, and run whatever applications you want, without ever touching your SSD; chainload it from the GRUB payload, or reconfigure coreboot to load Linux directly (from flash).
Jargon aside, one thing that many people will ask is: does Libreboot work with standard Linux/BSD systems, without modification? The answer is yes. Minifree uses standard Linux/BSD installer images, provided by the respective upstreams (e.g. Debian, Archlinux, FreeBSD). You can use your Libreboot machine more or less just as you would a typical BIOS/UEFI system; Windows is also compatible, though we recommend that you stick to Linux/BSD, for your freedom. More information is available on the Libreboot documentation.
These are the same machines used for Libreboot development. Leah Rowe, the founder and lead developer of Libreboot, also runs Minifree. Sales fund the project, and these machines are used by Leah day to day for all tasks. Many people are surprised when they turn on a Libreboot machine, and it gets to the bootloader (e.g. GRUB) in a few seconds or less, booting faster than even a brand new (non-Libreboot) machine. This is the power of Libreboot, and free software in general, in allowing the hardware to run much more efficiently.
Put simply: we want to live in a world where everyone can easily and comfortably use free software, liberated from the shackles of proprietary software. We want to live in a world where your property is your property; extended to computing, this makes free software a fundamental right that everyone must have.
Libreboot also provides a U-Boot payload these days on x86-64, present since Libreboot 20241206; it will be further developed in subsequent Libreboot releases. U-Boot provides a sensible UEFI implementation, but it’s very new; Libreboot still recommends the GRUB payload for the forseeable future, as it’s more stable and provides a lot more security features. MInifree ships with the GRUB payload by default.
Markdown file for this page: https://minifree.org/product/libreboot-t480.md
This HTML page was generated by the Libreboot Static Site Generator.
Email us if you wish to buy